Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a common virus that can lead to various health issues, including cervical cancer. Understanding the link between HPV infections and cervical cancer is crucial for prevention, early detection and treatment. In this article, we will explore the connection between HPV and cervical cancer, discuss the HPV vaccine and provide information about cervical cancer symptoms, diagnosis and treatment options.
Understanding HPV and Cervical Cancer
HPV is a group of more than 200 related viruses, with over 40 types that are transmitted through direct sexual contact. HPV infections are incredibly common; in fact, most sexually active individuals will contract at least one type of HPV at some point in their lives. While many HPV infections go away on their own without causing any health problems, some can persist and lead to serious conditions, including cervical cancer.
Cervical cancer is a type of cancer that occurs in the cells of the cervix, the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. Almost all cases of cervical cancer are caused by persistent infections with high-risk HPV types. Two specific types, HPV 16 and HPV 18, are responsible for approximately 70% of cervical cancer cases.
The HPV Vaccine
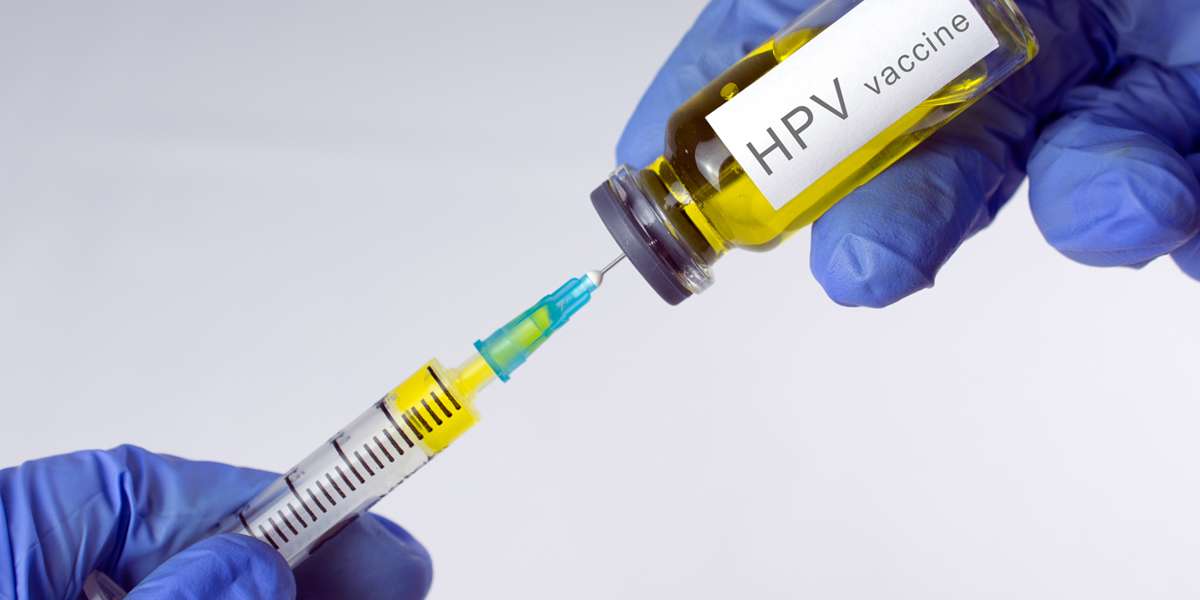
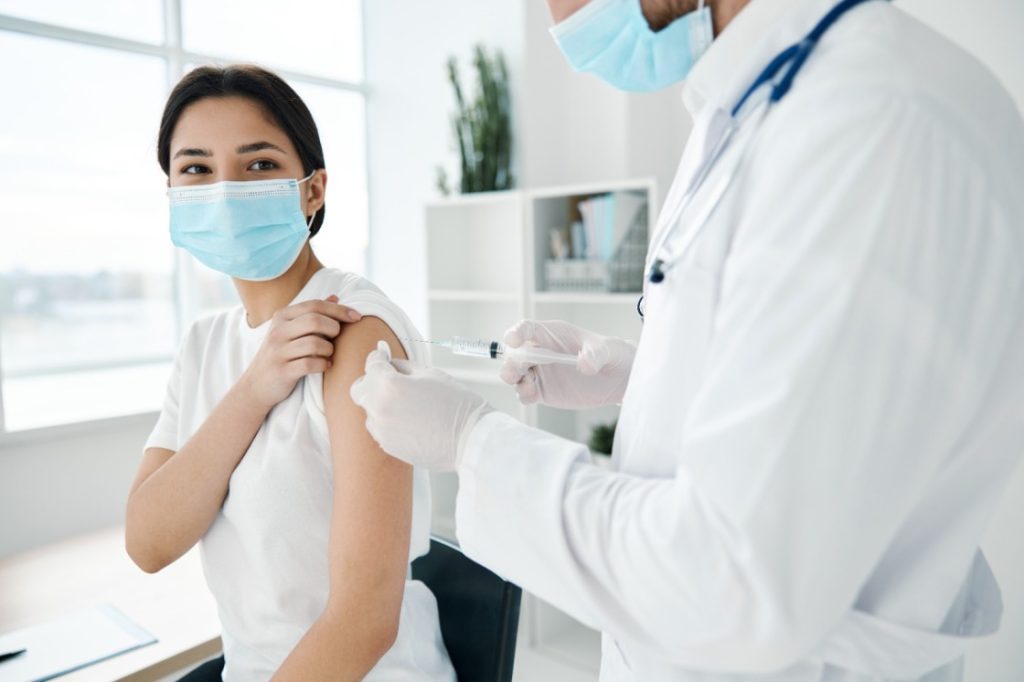
The HPV vaccine is a significant advancement in the fight against cervical cancer. It is designed to protect against the high-risk HPV types that cause most cervical cancers. The vaccine is most effective when given before individuals become sexually active, as it prevents HPV infections rather than treating existing ones.
There are three HPV vaccines available: Gardasil, Gardasil 9 and Cervarix. Gardasil and Gardasil 9 protect against HPV types 16 and 18, as well as other types that cause genital warts. Cervarix protects against HPV types 16 and 18. Vaccination is recommended for both boys and girls, typically starting at ages 11 or 12, but it can be administered as early as age 9 and up to age 45 in some cases.
Symptoms and Signs of Cervical Cancer
In its early stages, cervical cancer often does not cause noticeable symptoms. This is why regular screening through Pap tests and HPV tests is essential for early detection. As the cancer progresses, symptoms may become more apparent. Common signs and symptoms of cervical cancer include:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding: This can include bleeding between periods, after sexual intercourse or after menopause.
- Unusual vaginal discharge: The discharge may be watery, pink or foul-smelling.
- Pelvic pain: Persistent pain in the pelvis or lower back can be a symptom.
- Pain during intercourse: Discomfort or pain during sexual activity may occur.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare provider for evaluation and possible testing.
Preventing HPV and Cervical Cancer
Prevention plays an important role in reducing the risk of HPV infections and cervical cancer. By understanding and implementing effective preventive measures, individuals can protect themselves and reduce the incidence of these conditions. Here are some key strategies for preventing HPV and cervical cancer:
- HPV vaccination: As mentioned earlier, the HPV vaccine is highly effective in preventing infections with the high-risk HPV types that cause most cervical cancers.
- Regular screening: Routine Pap tests and HPV tests can detect abnormal cells early, allowing for timely intervention and treatment.
- Safe sexual practices: Using condoms and limiting the number of sexual partners can reduce the risk of HPV transmission.
- Avoiding tobacco use: Smoking is linked to an increased risk of cervical cancer, so avoiding tobacco can help reduce this risk.
HPV Symptoms and Treatment
HPV infections often do not cause any symptoms and can go unnoticed. However, some individuals may develop genital warts or other symptoms depending on the type of HPV.
- Genital warts: These are small, flesh-coloured or grey growths that appear in the genital area. They can be treated with topical medications, cryotherapy (freezing) or surgical removal.
- Precancerous changes: High-risk HPV types can cause changes in cervical cells that may be detected through screening tests. Treatment for precancerous changes can include procedures to remove or destroy the abnormal cells, such as cryotherapy, laser therapy or loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP).
It is important to note that there is currently no cure for HPV, but many infections go away on their own. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications.
Book Your HPV Vaccination for Cervical Cancer Prevention
The link between HPV infections and cervical cancer is well-established, with high-risk HPV types causing the majority of cervical cancer cases. The HPV vaccine is a powerful tool in preventing these infections and reducing the incidence of cervical cancer.
Regular screening, early detection and prompt treatment are essential for managing cervical cancer and improving outcomes. By understanding the connection between HPV and cervical cancer and taking preventive measures, we can work towards reducing the impact of this disease on women’s health.
Protect your health and take proactive steps against cervical cancer. Schedule your HPV vaccination today. Our expert team at Touchwood Pharmacy is here to guide you through every step, ensuring you have the best protection possible. Book an appointment with us today.