Headaches, a common malady affecting millions worldwide, can stem from various causes, from stress to dehydration. However, one underlying condition often associated with severe headaches is viral meningitis. Meningitis, an inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, can be caused by viruses, bacteria or other pathogens.
Among these, viral meningitis stands out for its potential to induce debilitating headaches. In this article, we discuss the relationship between viral meningitis and headaches, exploring its manifestations, underlying mechanisms and management.
Understanding Viral Meningitis
Viral meningitis, also known as aseptic meningitis, primarily results from viral infections. Enteroviruses, such as the Coxsackie and echoviruses, account for the majority of viral meningitis cases, although other viruses like herpes simplex virus, HIV and West Nile virus can also be implicated.
As viral meningitis is contagious, the transmission typically occurs through respiratory secretions or fecal-oral routes, highlighting the importance of hygiene and preventive measures.
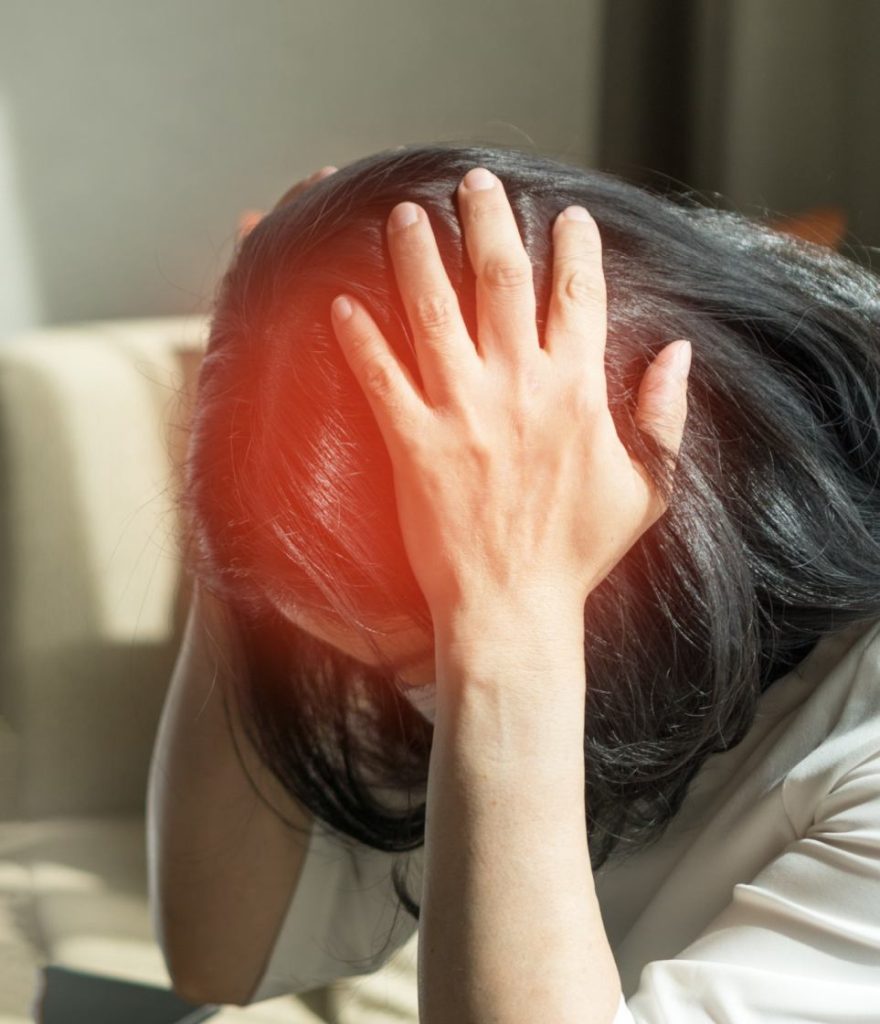
Viral meningitis symptoms may include severe headaches, fever, neck stiffness, nausea, vomiting, sensitivity to light (photophobia) and altered mental status. These symptoms may vary in severity and can mimic those of other illnesses.
The Headache Connection
Headaches represent a hallmark symptom of viral meningitis. These headaches often manifest as intense and persistent, characterised by throbbing or pulsating sensations. Patients frequently describe them as severe, often worsening with movement or exposure to light (photophobia) and sound (phonophobia). Such headaches can significantly impair daily functioning, leading to decreased productivity and quality of life.
Underlying Mechanisms on Link Between Viral Meningitis And Headaches
The link between viral meningitis and headaches can be elucidated through several underlying mechanisms. Firstly, the inflammation of the meninges, triggered by viral invasion, leads to increased intracranial pressure, causing headache symptoms.
Additionally, the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and mediators in response to the viral infection can sensitise pain pathways within the brain, intensifying headache perception.
Furthermore, viral-induced vasculitis, characterised by inflammation of blood vessels, may contribute to headache pathogenesis by disrupting normal blood flow regulation in the brain.
Diagnostic Challenges
Diagnosing viral meningitis solely based on headache symptoms can be challenging due to its nonspecific nature. Healthcare professionals often rely on a combination of clinical evaluation, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis via lumbar puncture and imaging studies to confirm the diagnosis.
CSF analysis typically reveals elevated white blood cell count and protein levels, along with normal glucose levels, aiding in differentiating viral meningitis from bacterial etiologies.
Management Strategies Headaches Due to Viral Meningitis
Managing headaches associated with viral meningitis encompasses a multifaceted approach aimed at alleviating symptoms and addressing the underlying viral infection. Analgesics such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can provide symptomatic relief from headaches.
However, caution must be exercised when administering NSAIDs, especially in patients with underlying medical conditions or those at risk of gastrointestinal complications.
In addition to pain management, antiviral medications may be prescribed in certain cases, particularly when specific viral pathogens are identified. Supportive care, including hydration and rest, plays an important role in facilitating recovery and minimising complications. Patients with severe symptoms or complications, such as seizures or neurological deficits, may require hospitalisation for close monitoring and specialised interventions.
Preventive Measures
Preventing viral meningitis involves adopting preventive measures to reduce the risk of viral infections. Practising good hand hygiene, avoiding close contact with individuals exhibiting symptoms of respiratory or gastrointestinal illnesses and ensuring vaccination against vaccine-preventable viruses (e.g., measles, mumps, rubella) can help mitigate the risk of viral meningitis transmission.
Additionally, promoting overall health and immunity through balanced nutrition, regular exercise and adequate sleep can bolster the body’s defences against viral infections.
Final Words
The link between viral meningitis and headaches underscores the importance of early recognition, prompt diagnosis and appropriate management of this potentially serious condition. By understanding the underlying mechanisms and implementing preventive measures, healthcare providers can effectively mitigate the burden of viral meningitis-associated headaches, improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Vigilance, education and collaborative efforts are paramount in navigating the complexities of this interplay and providing optimal care for affected individuals.
Book your vaccine appointment in the UK at Touchwood Pharmacy for timely protection. Ensure your health and safety with convenient access to vaccines. Schedule your appointment today for peace of mind.