Meningitis is caused by both bacteria and viruses – there are several different types. The main ways to spread meningitis are sneezing, coughing, kissing and sharing utensils and cutlery. Some people carry the virus or bacteria in their nose or throat but are not made ill by it so this is why it can be spread inadvertly. These people are described as asymptomatic which means they are not showing any symptoms. The only way to protect against both the viral and bacterial form of meningitis is to have a meningitis vaccination. It is possible to have meningitis more than once and so vaccination is crucial to protect against this disease.
What are the symptoms of bacterial meningitis?
These are the symptoms of meningitis and they can appear in any order. Some may not be present at all in the early stages:-
- fever or high temperature
- cold feet and hands
- vomiting
- rapid breathing
- aching joints and muscles
- confusion
- mottled skin
- headache and/or stiff neck
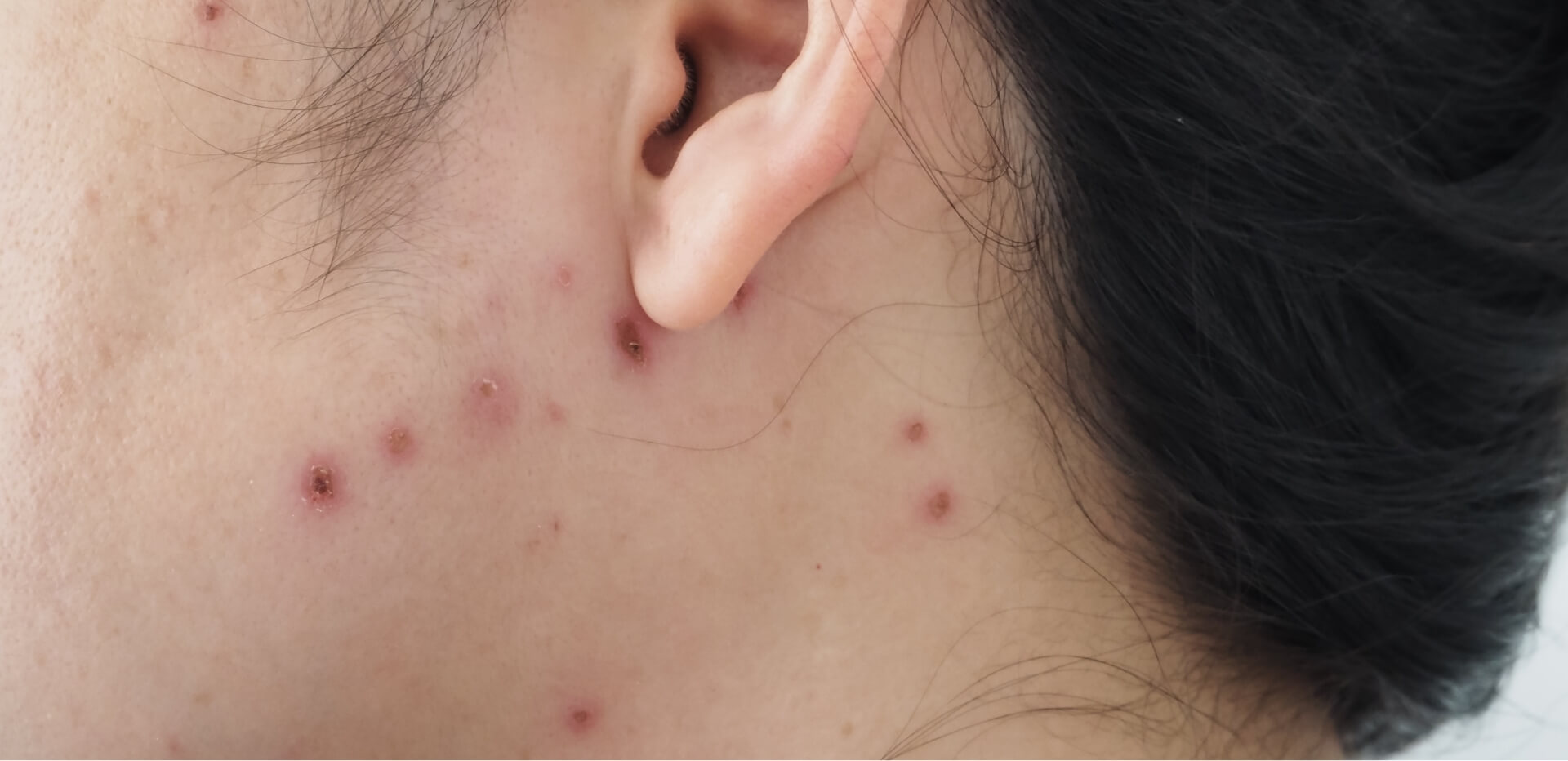
- spots or a rash
- sensitivity to bright lights
What is the treatment for bacterial meningitis?
Bacterial meningitis is very serious and tests will be carried out to determine whether the cause is viral or bacterial but hospital admission is not usually delayed because the outcome of bacterial meningitis can be so serious. Treatment is with antibiotics which are usually started before the diagnosis is confirmed.
How to prevent meningitis
Preventing meningitis follows some good practices which apply to other viral illnesses like Covid-19.
- Wash your hands – after using the toilet and after spending time in crowded public places
- Follow good hygiene – don’t share straws, drinks, food, eating utensils or toothbrushes
- Cover your mouth – if you need to cough or sneeze then cover your mouth
Not all forms of meningitis are preventable by vaccination but there are some of the meningitis vaccination which are recommended by healthcare professionals.