What is yellow fever and how it is caused?
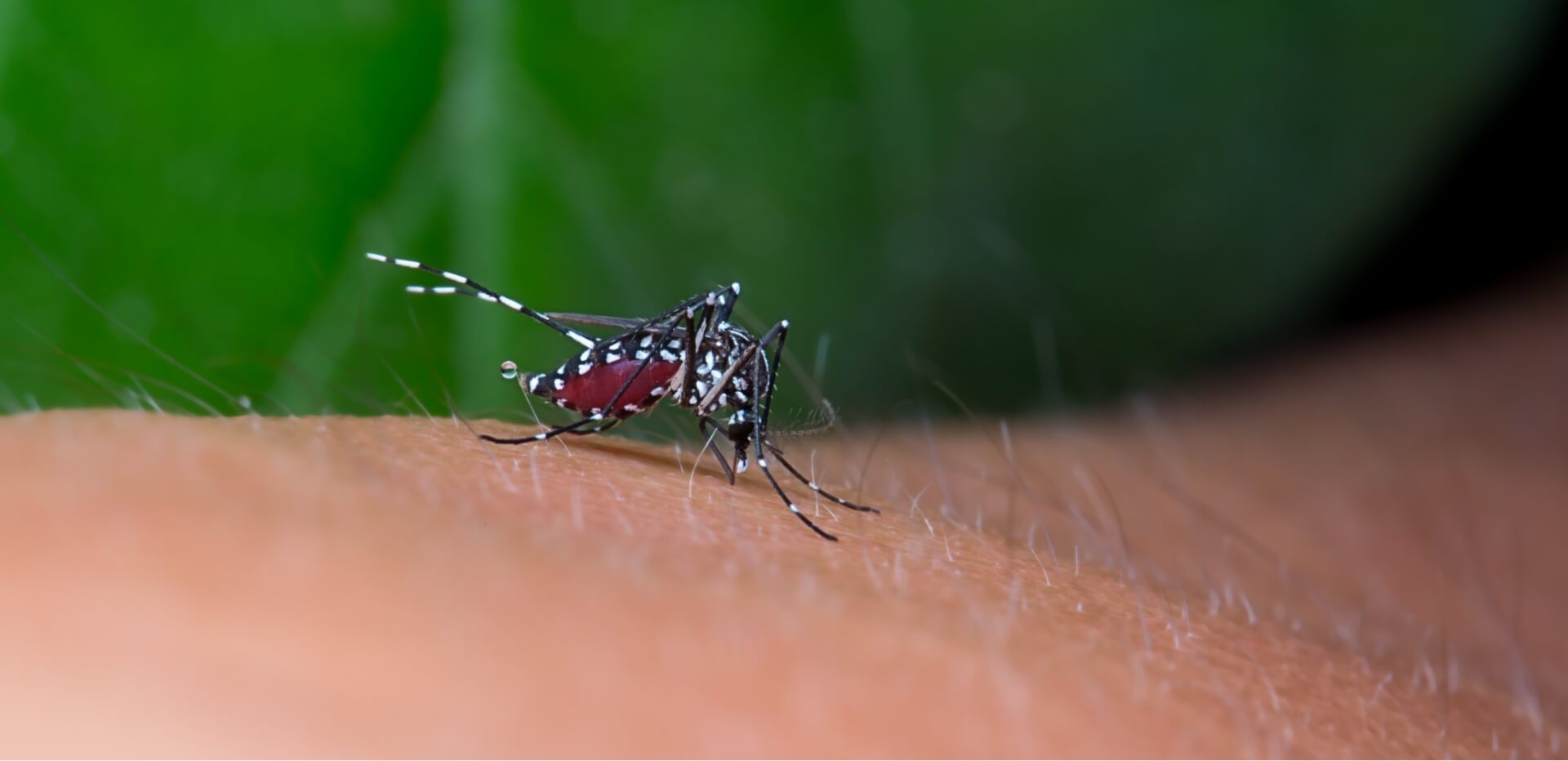
Yellow fever is a serious viral disease found in tropical regions of Africa and South America causing severe illness leading to liver failure and even death It is transmitted to humans through the bites of infected mosquitoes, particularly during the rainy season. It is highly recommended to get vaccinated for anyone who are planning to travel to the high-risk areas of yellow fever as it is a key preventive measure against this potentially fatal infection. Many countries require proof of yellow fever vaccination to be presented before you can gain entry to the country.
What are the signs and symptoms of yellow fever?
The symptoms of yellow fever begins with mild fever, chills, severe headache, back pain, body aches, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and weakness. These typically last for 3 to 4 days. While most people recover after this stage, a small percentage may develop more severe symptom such as yellowing of the skin and eyes, dark urine, abdominal pain, and bleeding from the eyes, nose, mouth, or stomach which can be fatal if this goes untreated.
About yellow fever vaccination
Stamaril® live vaccine is widely used for yellow fever vaccination, offering lifelong protection with just one dose against the disease. It is generally safe for anyone above aged 9 months and older. However, it is not recommended for individuals who have low immunity. Consult your pharmacist or doctor if you are concerned about your suitability for vaccination.
What are the common side effects of yellow fever vaccine?
The common side effects of yellow fever vaccine include fever, headache, joint and muscle pain, nausea, and soreness at the injection site. These effects usually occur anywhere from the day of vaccination up to 14 days and the serious side effects are very rare.
Is yellow fever vaccine safe?
Yes, the yellow fever vaccine is considered safe for most of the individuals aged over 9 months without major side effects. While there are rare cases of serious side effects have been reported in elderly people above 60-year-olds and those with weakened immune systems. It is important to get vaccinated when traveling to the regions where yellow fever is prevalent.
Which countries have high risk of yellow fever?
The are several countries are identified as having a high risk of yellow fever transmission.
In Africa – Angola, Benin, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Congo, Cote d’Ivoire, Democratic Republic of Congo, South Sudan, Sudan, and Uganda.
South America – Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, French Guiana, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay, Venezuela (Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela)
Other regions – Panama, Trinidad and Tobago
Vaccine advice and requirements are constantly under review, and you should speak to your pharmacist well in advance of any planned travel to ensure that you are meeting the most up to date advice.
Is yellow fever card necessary to travel?
Yes, in many cases, yellow fever card is necessary for international travel, particularly when visiting countries with a risk of yellow fever transmission. This proof of vaccination is often required by the receiving country to prevent the spread of the disease.
Does yellow fever card have expiration date?
Yes, yellow fever card does have an expiration date and their validity period can vary from 10 years to lifetime. In most cases, the certificate becomes officially valid 10 days after vaccination. To ensure hassle-free travel, it’s vital to verify destination country regulations regarding the validity of yellow fever vaccination certificates.
When is the best time to get vaccinated?
You must get vaccinated at least 10 days before you travel to high-risk areas of yellow fever. This timeframe allows the vaccine to take effect and provide adequate protection, as proof of vaccination is not valid until 10 days after receiving the vaccine. By planning ahead and ensuring you are vaccinated well in advance of your trip, you can mitigate the risk of contracting yellow fever.
How effective is the yellow fever vaccination?
The yellow fever vaccination is highly effective and safe with single dose providing lifelong protection for most individuals. A booster dose is typically recommended for specific groups, such as pregnant women, infants under 2 years old, or those with weakened immune systems.