Human Papillomavirus (HPV) infections are among the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs) worldwide. HPV can lead to various health problems, including genital warts and certain cancers. Understanding the causes and symptoms of HPV infections is crucial for prevention, early detection and effective management.
Causes of HPV Infections
HPV (Human Papillomavirus) infections are caused by the human papillomavirus. HPV is a group of more than 200 related viruses, some of which can lead to various health problems including genital warts and cancers.
- Sexual Contact: The primary mode of transmission for HPV is through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal and oral sex. The virus can be spread even when an infected person shows no signs or symptoms.
- Skin-to-Skin Contact: HPV can also be transmitted through close skin-to-skin contact, especially during intimate activities.
- Mother to Child: A pregnant woman with an active HPV infection can transmit the virus to her baby during childbirth.
- Indirect Contact: Although less common, HPV can be spread through contact with objects or surfaces that have been contaminated with the virus, such as shared sex toys.
Symptoms of HPV Infections
HPV (Human Papillomavirus) infections often do not cause any symptoms and can clear on their own without treatment. However, when symptoms do occur, they can vary depending on the type of HPV and the area of the body affected. Common symptoms of HPV infections include:
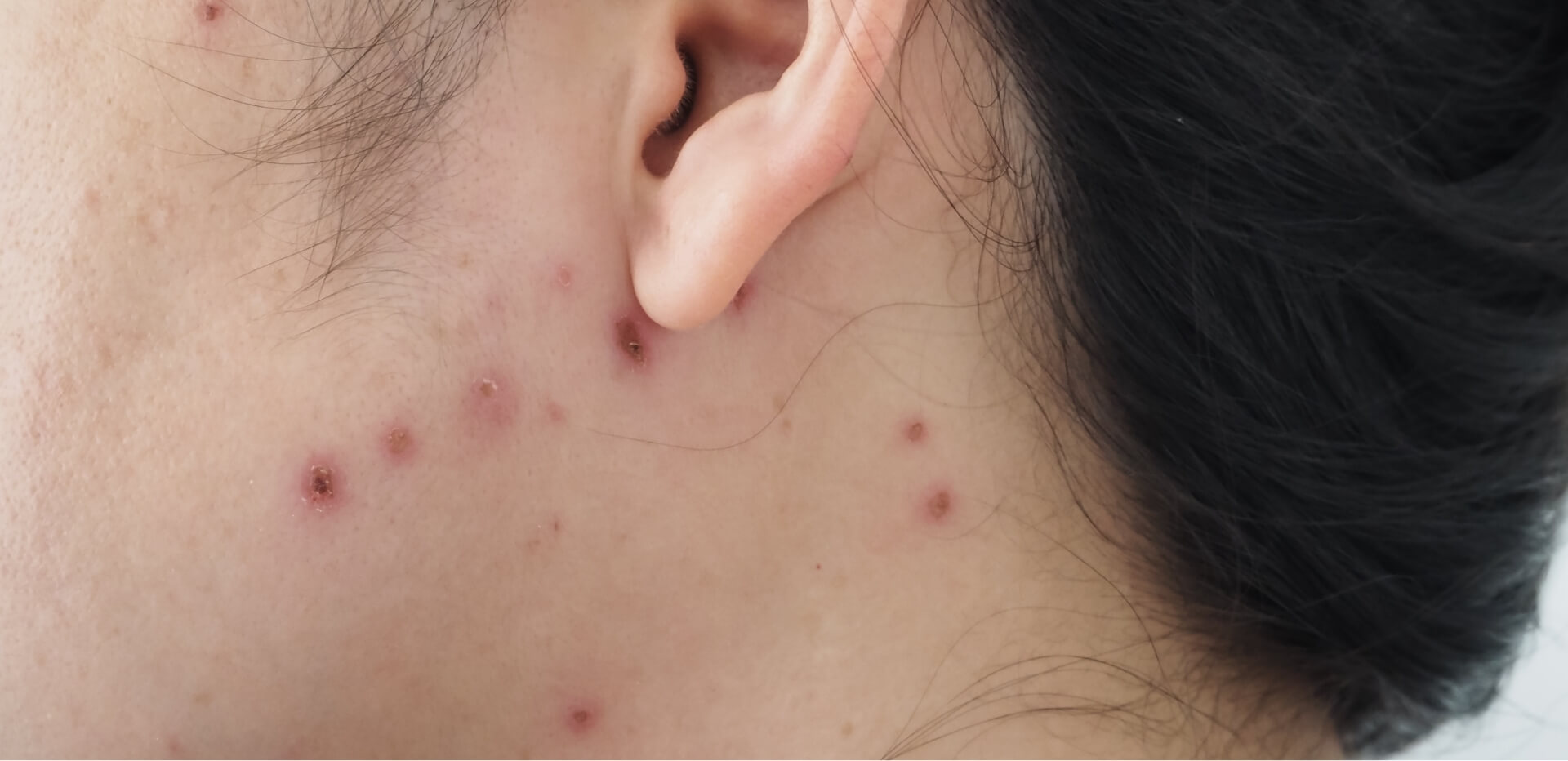
- Genital Warts: One of the most visible signs of an HPV infection is the appearance of genital warts. These warts can be small or large, raised or flat and can appear on the genitals, anus, mouth or throat.
- Respiratory Papillomatosis: HPV can cause benign tumours in the respiratory tract, leading to a condition known as recurrent respiratory papillomatosis (RRP). This condition can cause breathing difficulties and voice changes.
- Cervical Changes: HPV infections, particularly with high-risk strains, can lead to changes in the cells of the cervix, detectable through Pap tests. These changes may be precursors to cervical cancer.
- Cancer: Certain types of HPV are classified as high-risk because they can lead to cancers of the cervix, vulva, vagina, penis, anus and oropharynx (throat, tongue and tonsils).
- Asymptomatic Infections: It’s important to note that many individuals with HPV infections may not exhibit any symptoms at all. The virus can remain dormant in the body for years before causing any health issues.
Prevention and Management of HPV Infections
Prevention and management of HPV infections include several strategies:
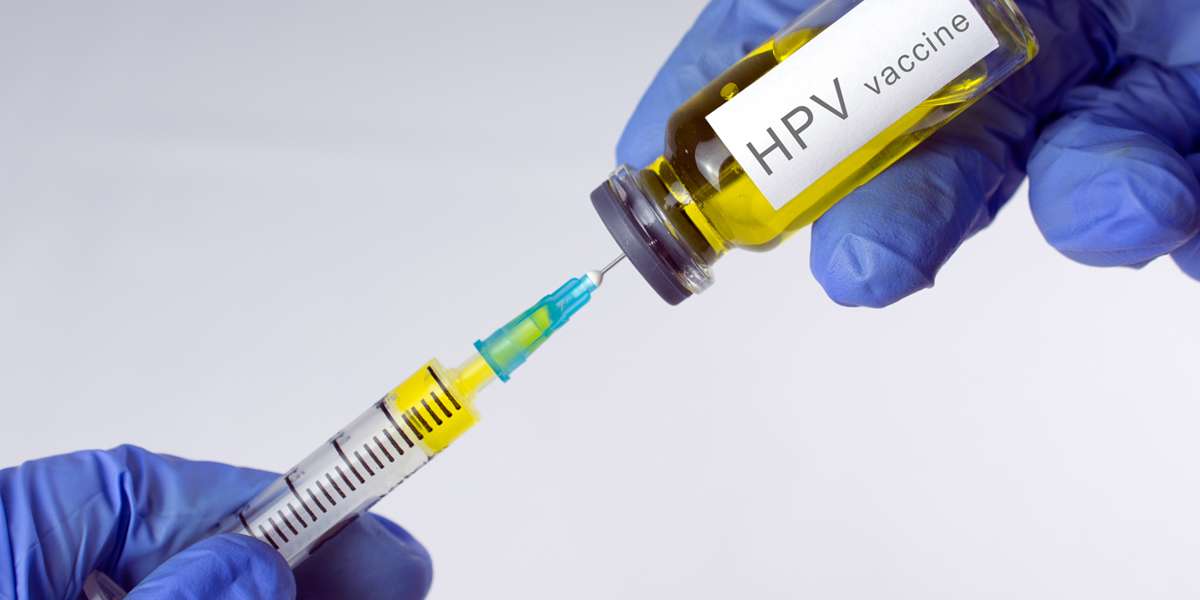
- Vaccination: The HPV vaccine is highly effective in preventing infections with the most common high-risk and low-risk HPV types. It is recommended for both males and females, ideally before they become sexually active.
- Safe Sexual Practices: Using condoms and dental dams can reduce the risk of HPV transmission, although they do not provide complete protection as HPV can infect areas not covered by these barriers.
- Regular Screenings: For women, regular Pap tests and HPV tests are crucial for early detection of cervical changes that may indicate a risk of cervical cancer.
- Limiting Sexual Partners: Reducing the number of sexual partners can decrease the likelihood of HPV exposure.
Protect Yourself Against HPV – Get Vaccinated Today
HPV infections are widespread and can lead to serious health problems, including cancer. Understanding the causes and symptoms of HPV is essential for prevention and early intervention. Vaccination, safe sexual practices and regular screenings are key strategies in managing the risk of HPV infections.
Don’t let HPV infections put your health at risk. Our expert team is here to provide you with a safe and comfortable vaccination experience. Book your appointment today and embrace a healthier, worry-free life.