Meningitis is a serious medical condition caused by the inflammation of the membranes (meninges) surrounding the brain and spinal cord. While it can affect anyone, children, teenagers, and those with weakened immune systems are particularly vulnerable. Understanding the early signs of meningitis and seeking immediate treatment is crucial, as the disease can escalate rapidly and lead to life-threatening complications.
There are two main types of meningitis: viral and bacterial, each with distinct causes and symptoms. Early recognition and treatment can make a significant difference in managing the condition effectively.
What are the Symptoms of Early Stage Meningitis?
The symptoms of meningitis can develop suddenly and progress quickly. In the early stages, many people mistake these symptoms for the flu, which can lead to dangerous delays in seeking treatment. Whether it is viral or bacterial meningitis, some early-stage symptoms are common across both types:
- High fever
- Severe headache
- Stiff neck
- Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
- Nausea and vomiting
- Confusion or difficulty concentrating
- Drowsiness or unresponsiveness
Viral Meningitis
Viral meningitis is the more common and usually less severe type. It’s often caused by various viruses, such as the enterovirus, which spreads through contact with an infected person or surface. The viral meningitis virus typically affects young children, but it can also impact adults.
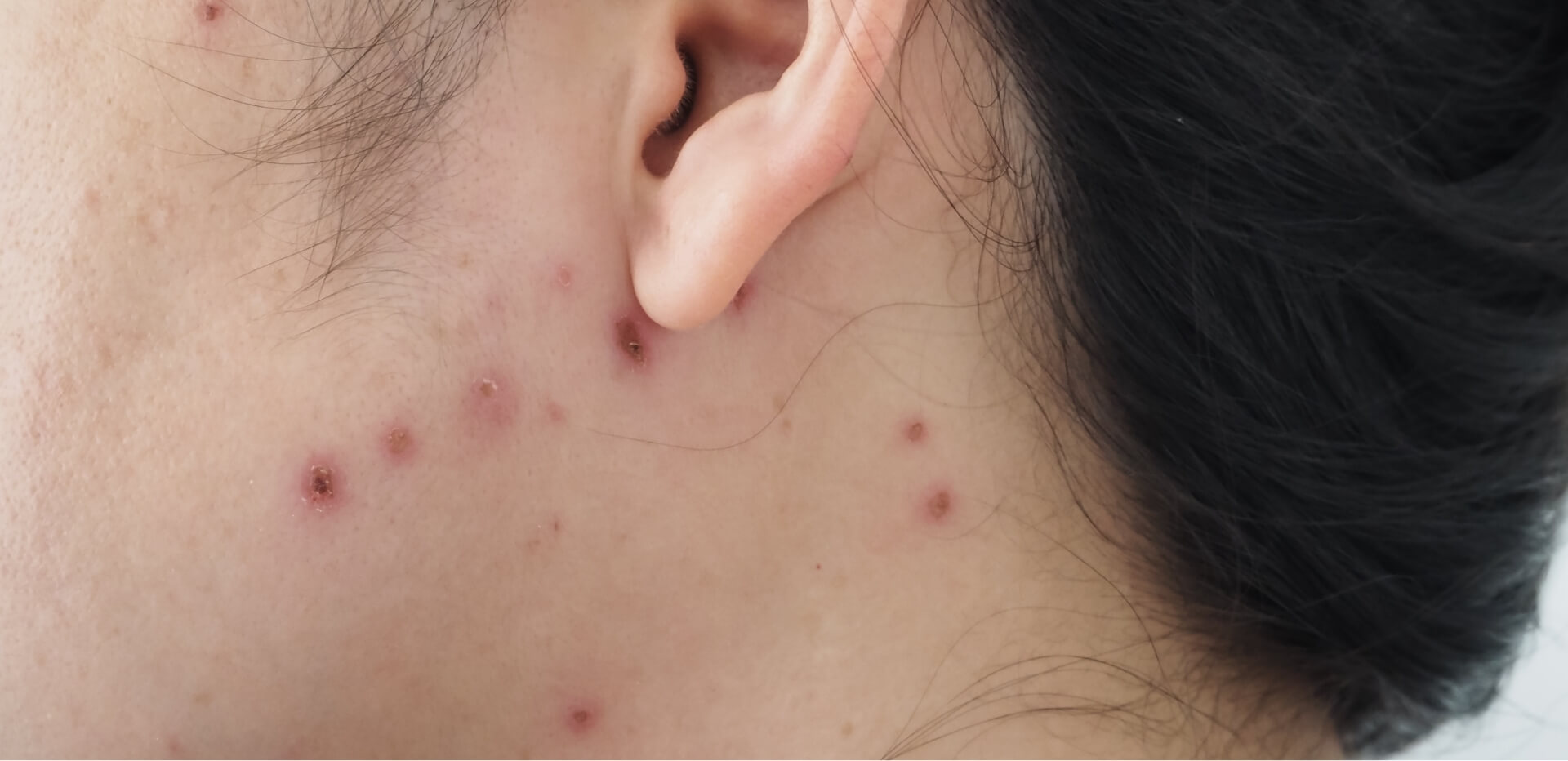
While viral meningitis is less aggressive than its bacterial counterpart, it can still cause uncomfortable and distressing symptoms. A notable symptom to watch for is the viral meningitis rash. This rash often appears as small red or purple spots that do not fade when pressed. Other symptoms of viral meningitis include:
- A headache that does not ease with painkillers
- Fatigue and general malaise
- Loss of appetite
- Muscle aches
In most cases, viral meningitis resolves on its own without the need for specific treatment, but some patients may require supportive care if their symptoms are particularly severe.
Treatment for Viral Meningitis
Viral meningitis typically does not require antibiotics, as they are ineffective against viruses. Instead, treatment focuses on managing symptoms and providing comfort. This might include:
- Resting in a quiet, dark room to reduce discomfort from light sensitivity
- Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids
- Taking over-the-counter painkillers like ibuprofen or paracetamol to reduce fever and ease headaches
- Using cool compresses to alleviate fever
In most cases, viral meningitis resolves within 7 to 10 days. However, if symptoms worsen or do not improve, it’s important to contact a healthcare provider.
Bacterial Meningitis
Bacterial meningitis is far more severe than viral meningitis and requires immediate medical intervention. This type of meningitis occurs when bacteria invade the bloodstream and infect the meninges. Common bacteria that cause this condition include Streptococcus pneumoniae and Neisseria meningitidis.
Bacterial meningitis can be life-threatening, and its symptoms can develop rapidly, sometimes within hours. Along with the early-stage symptoms like fever, stiff neck, and headache, bacterial meningitis can cause:
- Seizures
- Sudden unresponsiveness or coma
- Difficulty waking up or staying awake
- Severe muscle pain
- Cold hands and feet with a high body temperature
- Pale, blotchy skin or a rash that doesn’t fade when pressed (similar to viral meningitis)
Treatment for Bacterial Meningitis
Bacterial meningitis requires aggressive treatment, often starting before diagnostic tests are even completed. The main treatments include:
- Antibiotics: These are administered intravenously to target the specific bacteria causing the infection. The type of antibiotic used depends on the bacteria responsible.
- Corticosteroids: Steroids may be given to reduce inflammation around the brain and prevent further damage.
- Fluids and oxygen therapy: To ensure the body remains hydrated and that the brain receives enough oxygen.
- Hospitalisation: Severe cases may require intensive care, where the patient can be closely monitored for any complications.
How to Prevent Meningitis?
The good news is that meningitis can be prevented in many cases, especially bacterial meningitis, through vaccination. Vaccines are available for several of the bacteria that cause the disease, including the meningococcal, pneumococcal, and Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) vaccines.
Maintaining good hygiene, such as regular handwashing and avoiding contact with sick individuals, can also help prevent the spread of viral meningitis. People in close contact with someone who has bacterial meningitis may be given antibiotics as a preventative measure.
Stay Protected: Book Your Vaccine Appointment Today!
Meningitis is a serious condition that requires prompt attention, especially since its symptoms can resemble those of less severe illnesses. Recognising early signs and understanding the differences between viral and bacterial meningitis can make an important difference in treatment and recovery.
The best way to protect yourself and your loved ones is through vaccination and early action. If you are concerned about meningitis or would like to learn more about protecting yourself and your family, book an appointment with one of our vaccine specialists at Touchwood Pharmacy. Our experts can provide you with up-to-date information on available vaccines and help you stay protected against meningitis and other serious diseases.